Endoscopic Intragastric Balloon
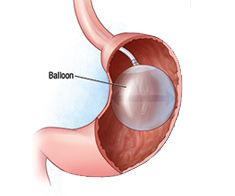
The intragastric balloon (IGB), also known as the endoscopic gastric balloon, is a non-surgical weight loss procedure which is performed under sedation in a Day Surgery Clinical setting. It involves the insertion of a specialized silicone balloon inside the stomach which is then subsequently filled with normal saline (sterile water) and methylene blue dye. The IGB takes up a considerable amount of space, thereby limiting the solid food carrying capacity of the stomach. This therefore makes you feel fuller sooner, and so individuals often find that their solid food portions are reduced, resulting in a reduction in overall calorie intake and hence some weight loss.
It is recommended that the IGB be endoscopically removed after 6 months in the stomach, to reduce the risk of complications. Often anti-obesity medication is prescribed prior to the balloon removal, to counteract the body’s hardwired tendency to want to regain weight (hence assisting with weight loss maintenance).
A suboptimal weight loss response:
- Partial-responders vs non-responders to treatment
- At present, there is no pre-operative testing that can be done to determine how you will respond to this or any particular therapy
- However, you might be suitable for add-on therapy eg anti-obesity medication or a variety of other surgical options
IGB Indications:
The IGB may be considered in patients:
- With a BMI ≥27 kg/m2
- Who did not respond to diet and exercise program alone
- Are willing to participate in a medically -supervised lifestyle and behavior modification program
IGB Contraindications:
The IGB is not permitted in patients:
- Who have previously undergone bariatric metabolic surgery
- Are suffering from inflammatory disease of the gastro-intestinal (GI) tract
- Have a large hiatus hernia
- Have structural irregularities in the pharynx, oesophagus
- Who are high risk or prone to GI bleeding
- Women who are/ are planning to fall pregnant
- Women who are currently breastfeeding
- Recent history of drug and/ or alcohol dependence
Risks & Complications of IGB placement
The IGB procedure is generally safe, but as with any procedure, complications may occur and include but are not limited to:
- Oesophageal or gastric ulceration
- Oesophageal or gastric perforation
- Deflation of the balloon which can lead to small bowel blockage, which becomes a medical emergency.
Please note, should the silicone balloon develop a leak or rupture, the blue dye will cause your urine to change colour. If this occurs, you should contact the Clinic immediately.











